Tackling Human-Wildlife Conflict and Illegal Pet Trade: How the LICIT Projects are Making a Difference
-

- by Indrani Sasmal April 25, 2023

Introduction
Human-Wildlife Conflict (HWC) has become a pressing issue in various regions across the globe, leading to devastating consequences for both wildlife and local communities. Besides the killing of animals that are perceived to be threatening livelihoods, another of the detrimental outcomes of HWC is its contribution to the Illegal Wildlife Trade (IWT). The prevalence of IWT in areas with already low populations of animals threatens the survival of numerous species, including cheetahs. CCF and its partners are addressing HWC and IWT with innovative community-focused projects that are making strides towards a sustainable coexistence between humans and wildlife in the Horn of Africa (HoA).
LICIT-II Project: Addressing the Gaps
To address the gaps identified in the LICIT project, CCF applied for the Legal Intelligence and Community Governance for Cheetah Illegal Trade (LICIT-II) project, which was funded by DEFRA’s IWT Challenge Fund in 2022 for three years.
Addressing the Root Causes of HWC and Illegal Pet Trade
When predators like cheetahs prey on livestock, the primary source of income for local communities, it leads to retaliation and HWC, increasing the motivation to capture cubs and sell them into the IWT. Reducing wildlife crime related to cheetahs and other wildlife in the HoA requires addressing both HWC and increasing enforcement action.
The LICIT-II project focuses on training farmers to manage their livestock and land and coexist with wildlife, strengthening wildlife crime task force information exchange across participant states, and improving legal frameworks in Somaliland and regionally. These components work together to achieve the long-term impact of reducing the IWT of live cheetahs (and other wildlife) in the HoA.
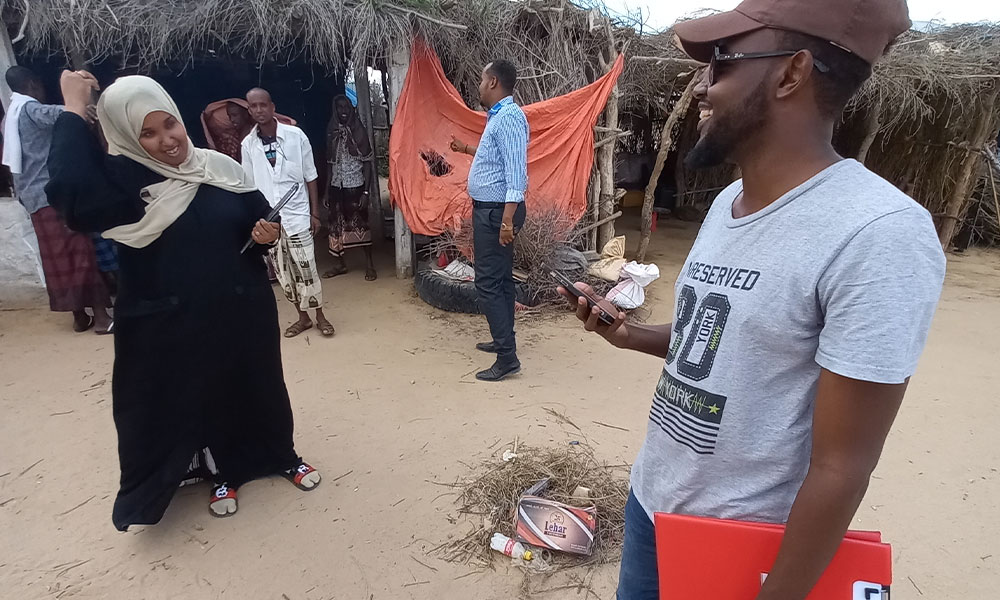
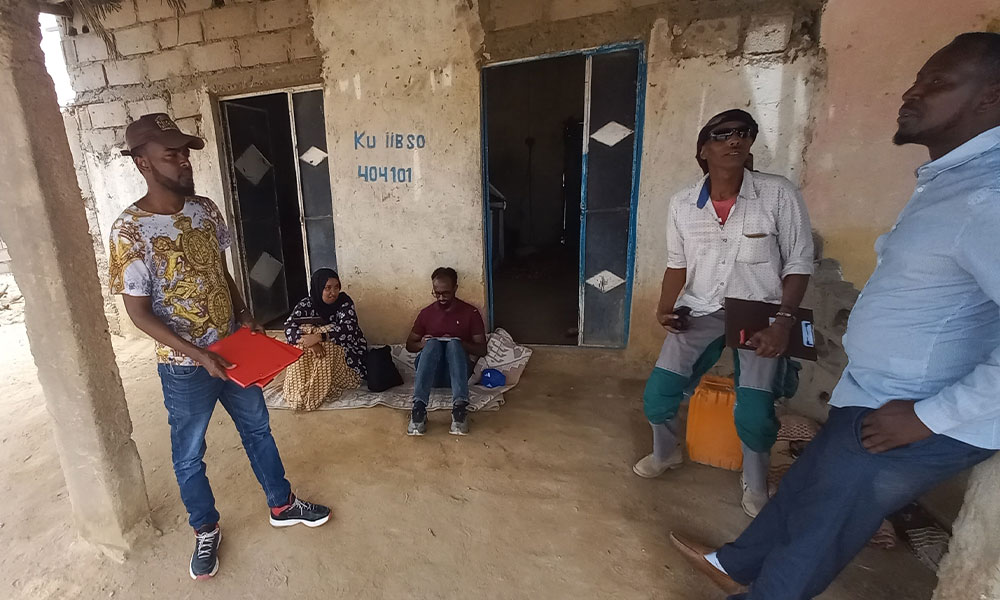
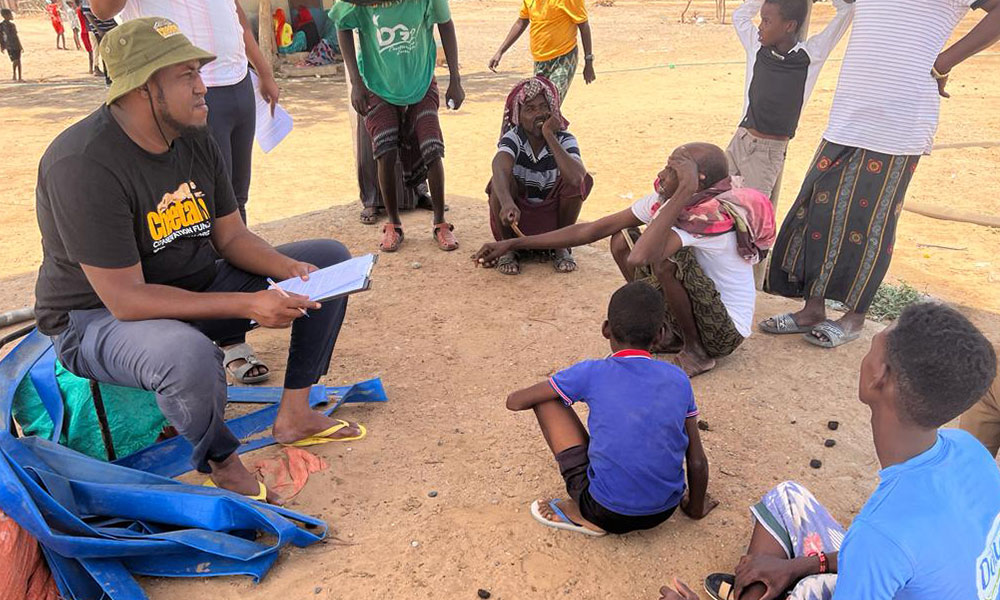
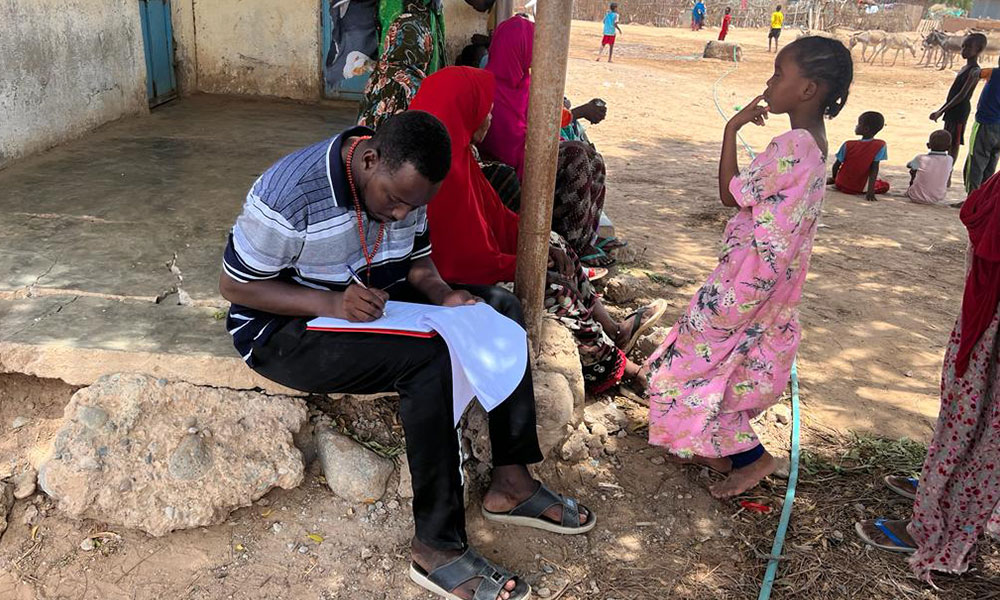
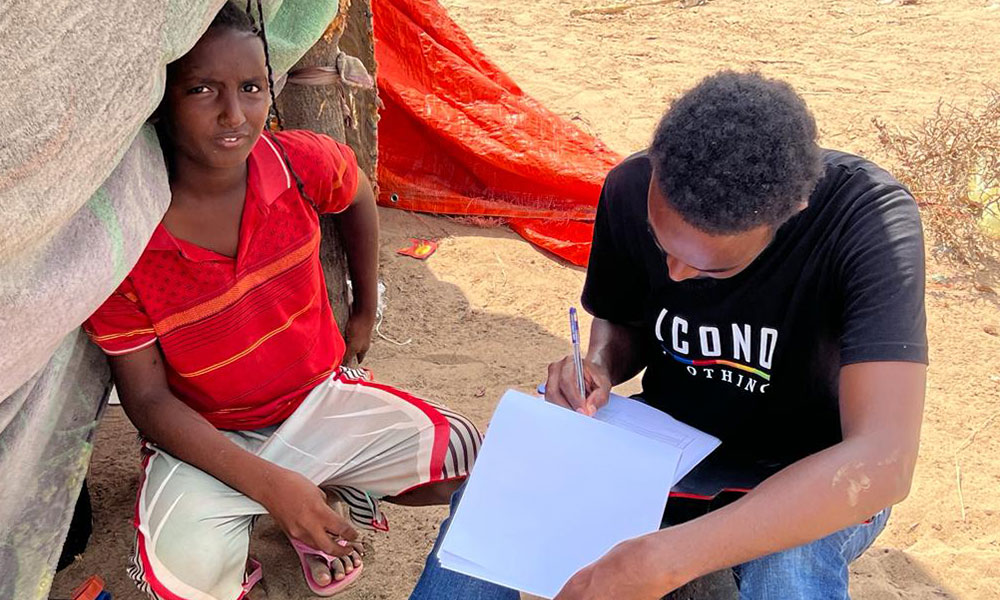
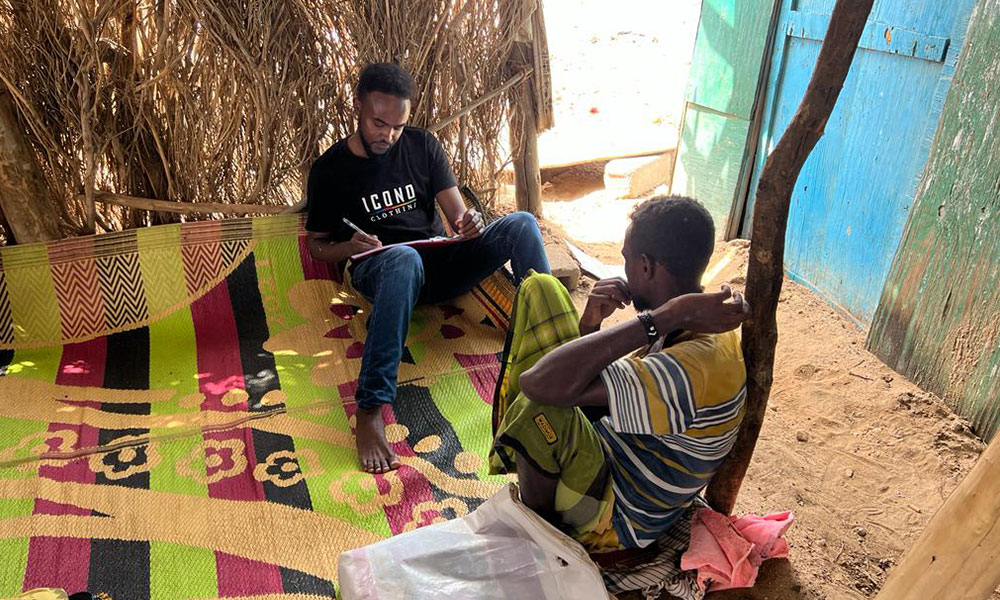
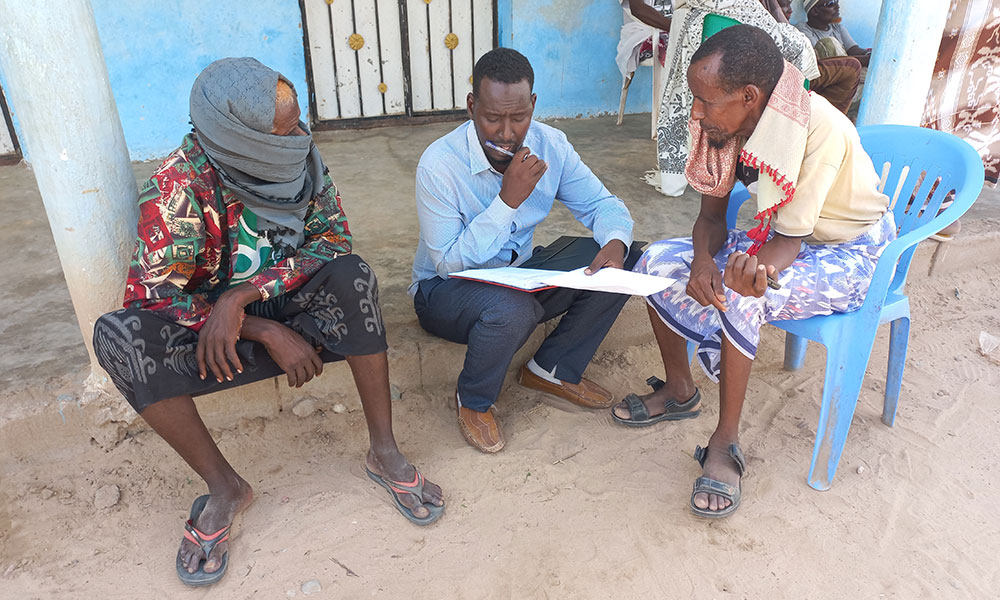
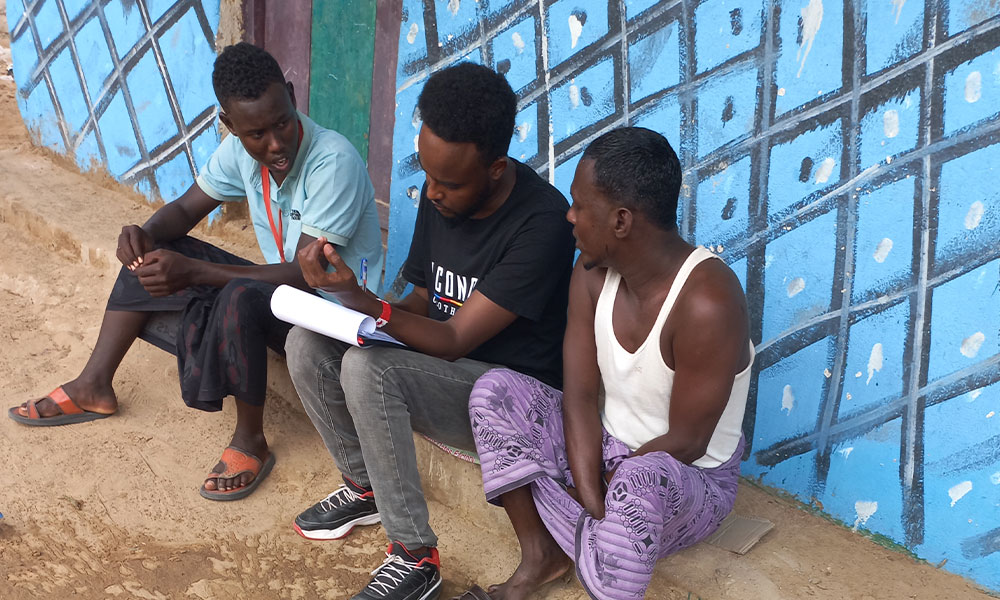
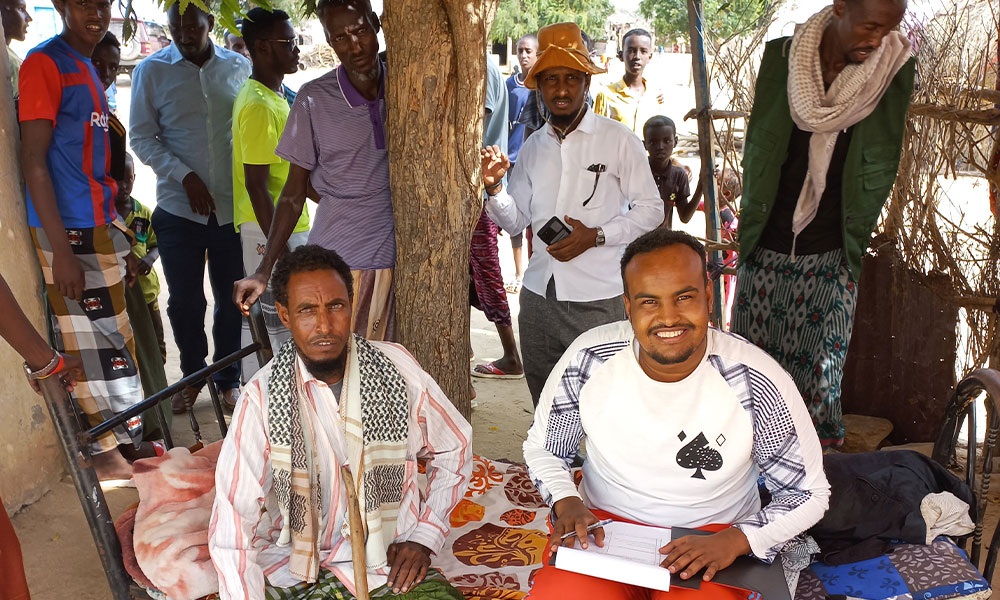
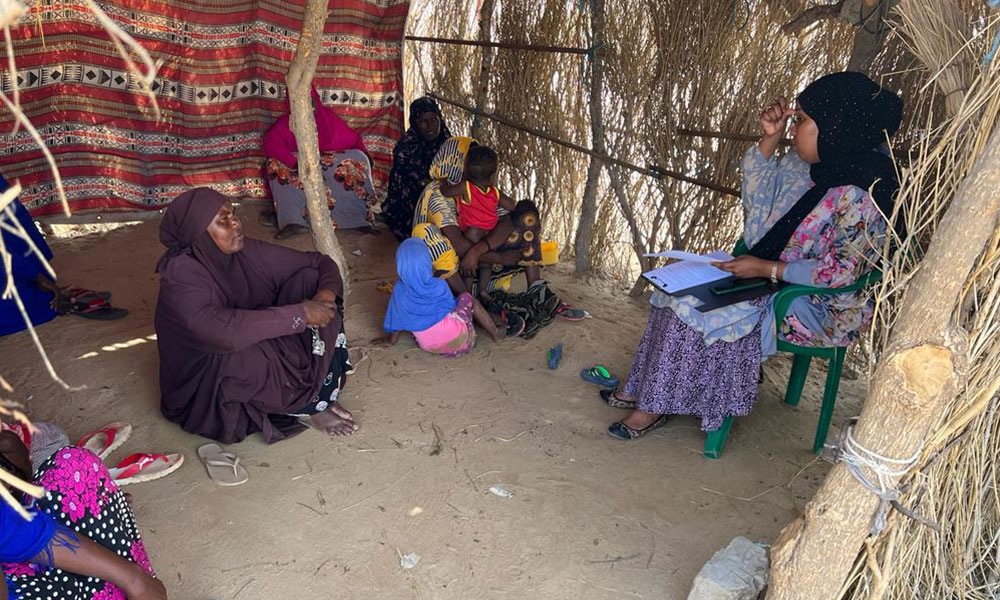
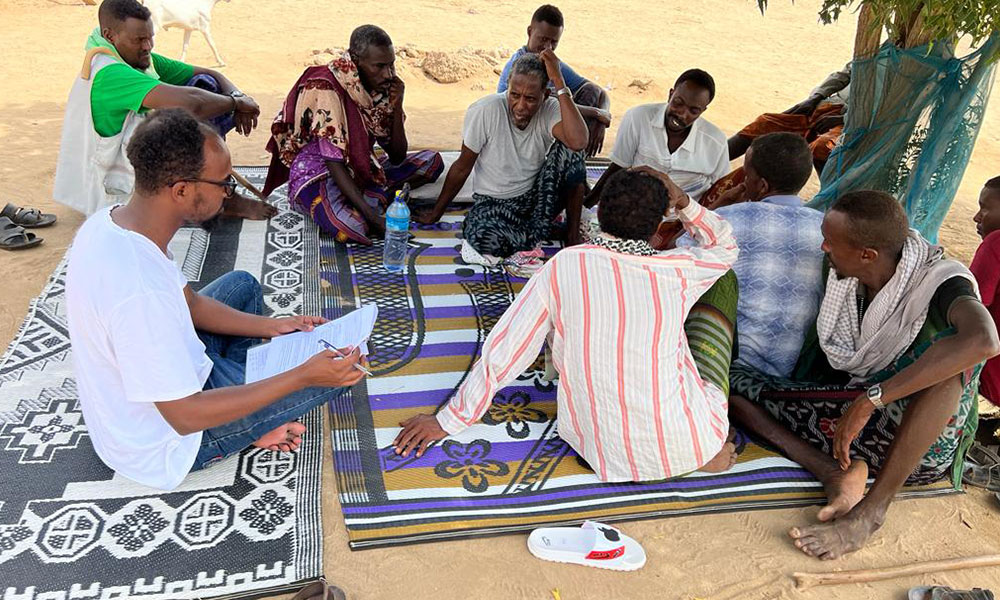
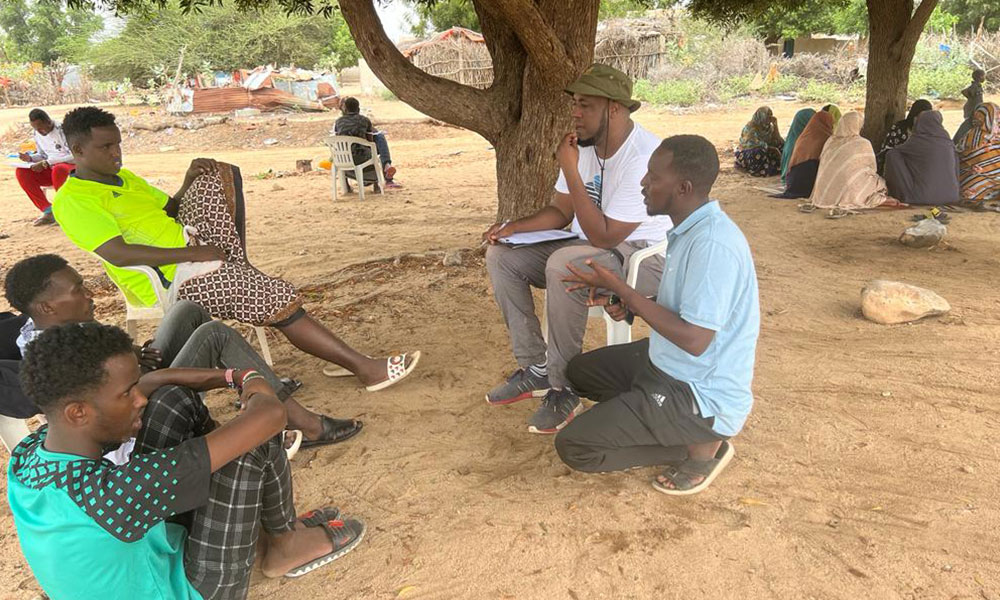
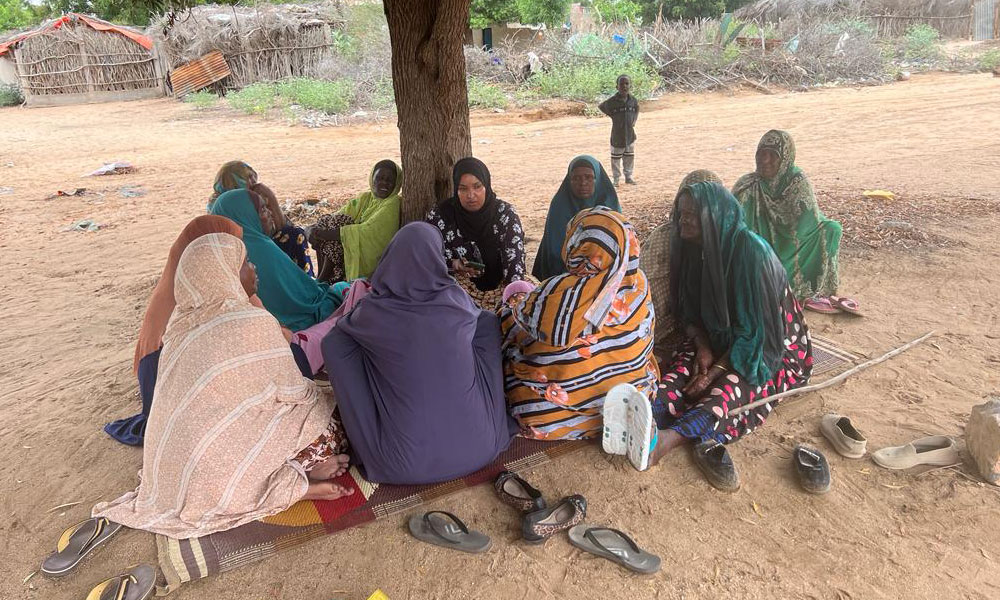
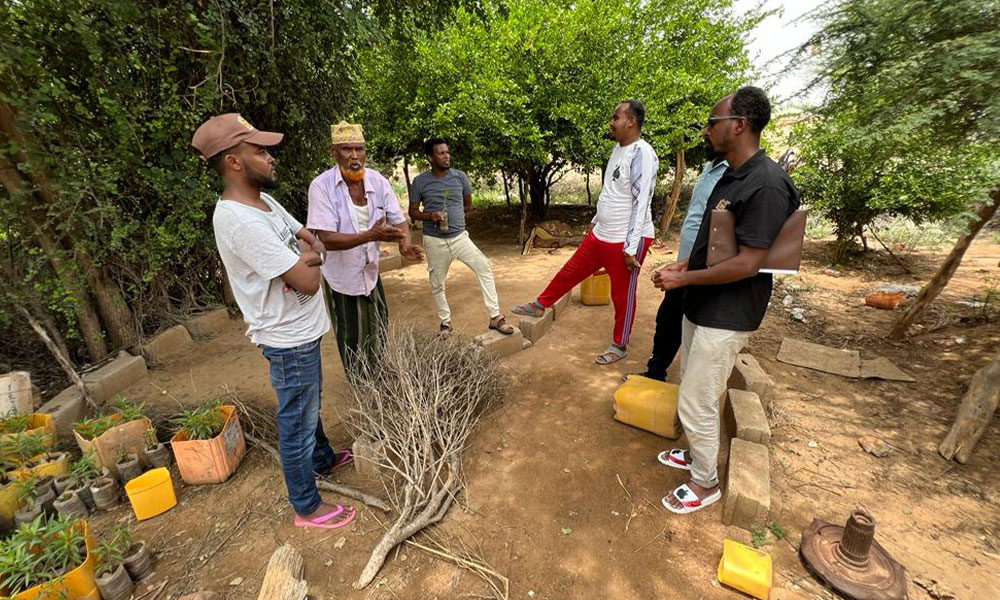
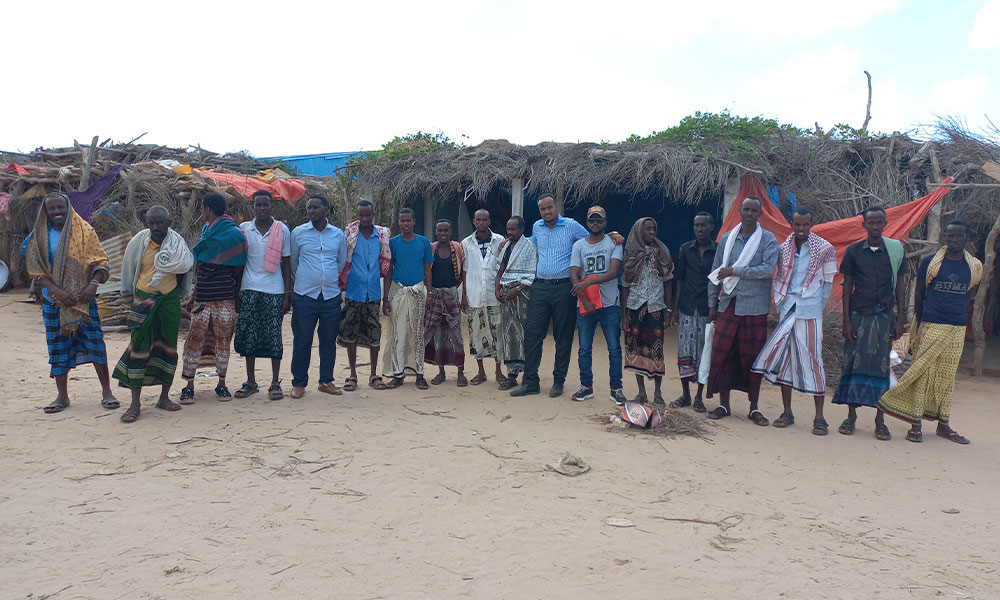
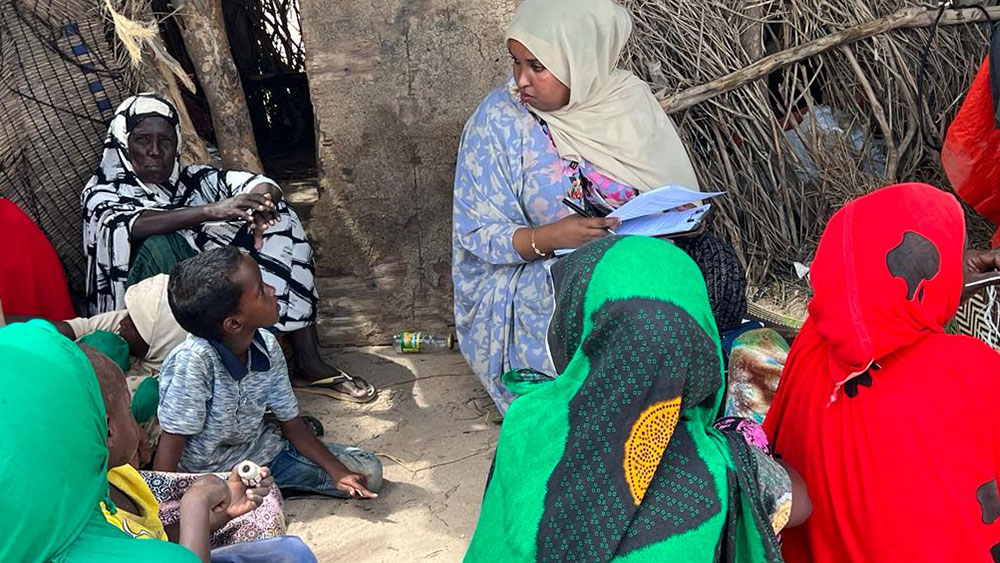
As part of LICIT-II CCF’s Education team in Somaliland completed community outreach and survey visits in Awdal during the first quarter of 2023.
A total of 7 villages were interviewed for the surveys as focus-group discussions:
- Village elders
- Adult men who are actively working in the village (pastoralists, small business etc.)
- Adult women who are actively working in the village
The LICIT-II project also aims to enhance national and regional capacity in the HoA to combat wildlife crime by leveraging gains made through LICIT (IWT-066). CCF is partnering with Legal Atlas (LA) and Trade Records Analysis of Flora and Fauna in Commerce (TRAFFIC), a global non-governmental organization, to execute the project activities. These activities include establishing a Community Conservation Governance Structure (CCGS) in the Awdal region of Somaliland, implementing CCF’s Future Farmers of Africa (FFA) program, exploring existing Environmental Crime Unit’s legal instruments, providing technical legal assistance to amend existing wildlife legislation, and expanding TRAFFIC’s online tool TWIX to improve cross-border cooperation.
Exploring TRAFFIC’s TWIX: A Key Tool for Wildlife Crime Information Sharing
TRAFFIC’s TWIX is a leading online tool designed for enforcement and management officials, facilitating swift information and expertise sharing within and across borders. This innovative platform has a successful track record in building robust information-sharing networks, which are crucial for combating wildlife crime.
As part of the LICIT-II project, TRAFFIC has already received support from the Ethiopian government to connect the Eastern Africa TWIX (EA-TWIX) to this initiative. The rollout will involve a scoping mission in Ethiopia to engage with stakeholders, establish a plan of action, and appoint TWIX focal persons. Additionally, TRAFFIC will deliver a national TWIX training workshop and provide follow-up support to focal persons on website usage.
TWIX
TRAFFIC’s TWIX plays a vital role in connecting enforcement and management officials, enabling efficient information exchange to tackle wildlife crime more effectively.
Due to its political standing, Somaliland cannot directly join the EA-TWIX, which prevents official data sharing. To overcome this challenge, TRAFFIC will develop a TWIX-compatible database template following TWIX best practices, allowing for future integration with the EA-TWIX network. This effort will be supplemented by the creation of a manual containing guidelines to prepare countries for joining TWIX.
Background on the LICIT Project
In 2019, the United Kingdom’s Department of Environment, Food and Rural Affairs (DEFRA) Illegal Wildlife Trade (IWT) Challenge Fund provided funding to CCF for the Legal Intelligence for Cheetah Illicit Trade (LICIT) project. This initiative aimed to identify gaps in the existing approach towards addressing IWT and HWC in the Horn of Africa (HoA), with a special focus on predators like cheetahs. CCF collaborated with the International Fund for Animal Welfare (IFAW) and Legal Atlas (LA) to execute the LICIT project.
Through the LICIT project, several weaknesses were identified in the existing approaches, such as inadequate ownership of natural resources by local communities, lack of proper land and herd management knowledge, and insufficiently organized governance structures. These shortcomings led to increased HWC and IWT of cheetah cubs. Additionally, a lack of wildlife crime information collection, inconsistencies in approach, and inadequate sharing between national agencies and across borders were also identified as weaknesses.

LICIT Project Funding
This project is funded by the UK government through its Illegal Wildlife Trade Challenge Fund.
Related Reading
-
January 20, 2024
Safeguarding Biodiversity with an Updated Conservation Bill





















